Types of mechanical waves
Mechanical waves can be classified by the direction in which atoms or molecules are temporarily displaced from their mean positions  relative to the flow of energy.
relative to the flow of energy.
Mechanical waves can be one of three types:
- longitudinal
- transverse
- torsional.
In this unit, we shall only consider the first two types. It is important to note that mechanical waves temporarily disturb a medium. The medium is not transported but the energy is.
A longitudinal wave is a disturbance in which the particles of the medium move in the same plane as the flow of energy (ie parallel or anti-parallel to the flow of energy).
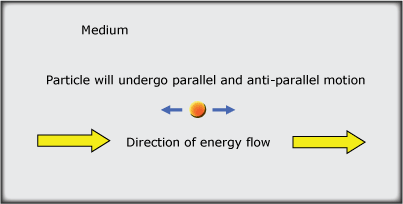
Particles (atoms or molecules) that make up a medium are not isolated. Neighbouring particles exert electrostatic forces on each other so a shift in a particle's position results in forces pushing or pulling the particle back to its mean position. A returning particle will overshoot its mean position, due to its inertia, before once again experiencing the push of neighbouring particles. This to-and-fro motion, or oscillation, is parallel and anti-parallel to the direction of energy flow.
Longitudinal waves are characterised by an alternating series of regions of closely spaced particles (compressions) and widely spaced particles (rarefactions).
The oscillating motion of the particles is shown in this animation.

Longitudinal waves can exist in solids, liquids and gases. A sound wave in air (eg thunder) is an example of a longitudinal wave.
A transverse wave is a disturbance in which the particles of the medium move in a plane perpendicular to the flow of energy.
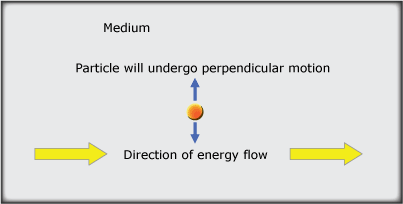
Transverse waves are characterised by a sinewave like appearance – even though the particles of the medium are always moving perpendicular to the direction flow as shown in the animation below.
View a transverse wave animation.

Mechanical transverse waves exist in solids and on the surface of liquids, but not in gases. The oscillation of a stretched string is an example of a transverse wave.

Word match
1 |
Choose the correct meaning for each wave-related term. |
Ocean waves
Not all waves are one type only. An example is wind-generated ocean waves.
View this animation of the true nature of these waves.


You may wish to consider the following as a group.
- Is a 'Mexican wave' at a sporting arena a mechanical wave? Discuss.
- How would you classify a small ocean wave – transverse or longitudinal? Explain.
- Can sound waves be transverse waves? Explain.
- Explain how a torsional wave disturbs a medium.





