Amino acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. The human body has 22 amino acids that are used for a variety of tasks. One of these is the creation of proteins, which the body builds by combining amino acids in a certain way. This task is guided by genetic information on our DNA, with the correct order of the amino acid units being vital for the effectiveness of the protein molecule being created.
Structure of amino acids
All amino acids contain two functional groups, -NH2 and -COOH. Watch the animation below to see an example of an amino acid.

Text alternative to the amino acid video
Animation showing an amino acid group within the structure of an amino acid (NH2CH2COOH).

Click here to open the video in a new window

You will see from the video that the -NH2 group is attached to the carbon atom next along from the -COOH group. This atom is called the α ( alpha ) carbon atom. Although there is a large range of possible amino acids, the important ones that are part of this course are all α amino acids. Below is an example of another α amino acid, aspartic acid.
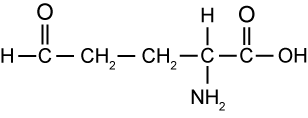
Aspartic acid is actually a diprotic  acid, but because the -NH2 functional group is attached to one of the α carbon atoms, it is classified as an α amino acid.
acid, but because the -NH2 functional group is attached to one of the α carbon atoms, it is classified as an α amino acid.
Read your Text "Chemistry for WA 2" section 12.4 and complete the Review Exercise
Based on the general structure of amino acids, predict the properties of amino acids by completing the following questions.
1 |
Amino acidsWhich of the following statements regarding amino acids are true? |